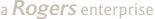Blue barred parrot Scarus ghobban
- Fringing Reef
Description
The Scarus ghobban, of the order of Perciformes and family Scaridae (Parrotfishes) is commonly known as the Blue-barred Parrotfish, Blue Trim Parrotfish, Blue-chin Parrotfish, Cream Parrotfish, Globe-headed Parrotfish, Green Blotched Parrotfish and Yellow Scale Parrotfish. The initial phase (female) of this species is a dull yellow-orange colour with five incomplete blue bars vertically across the body. The dorsal and anal fins are yellow with blue margins. Its caudal fin is emarginated. Sex change occurs at 29cm and 7 years of age. The terminal phase (males) are blue on the dorsal part and yellow on the sides. There is a blue bar on each scale and blue bands that extend backward from the eye. The dorsal and anal fins are yellow with blue margin. The caudal fin is of a lunar form[1]. This species has a total of 9 dorsal spines, 10 dorsal soft rays, 3 anal spines and 9 anal soft rays[2]. Parrotfish also possess teeth in both jaws that fuse to form a parrot like beak.
Habitat and ecology
This species is present across the Indo-Pacific region. It is found in lagoons and seaward reefs. It is often seen near drop offs and steep slopes. The recorded depth range is between 3 to 90m. Males are common in atolls while females have a preference for deeper habitats. They feed by scraping algae off the surface of rocks and corals.
Conservation and management
According to the IUCN Red list, this species is categorized as being of ‘Least Concern’. It is widely found in the Indian ocean and there are no major threats to the populations. No conservation measures are in place for this species. It is present in many MPAs though[1].
Did you know?
This species can reach a maximum recorded length of 90cm.